Voice assistants, facial emotional analysis and conversational data: essential tools for businesses
Published on September 09, 2024 - Updated on September 09, 2024
Voice assistants, facial emotional analysis and conversational data: essential tools for businesses
Discover how facial, voice and conversational emotional analysis can improve understanding of customer emotions. Explore the challenges, technologies and practical applications for customer services, and find out how Q°emotion meets these needs.
1. The evolution of voice assistants: towards more emotional interactions

Voice assistants, such as Alexa, Google Assistant or Siri, have become key elements of our daily lives. They help us manage our diaries, set alarms, answer our questions and control our connected homes. But today, their role goes beyond these simple tasks: they are becoming capable of detecting and reacting to our emotions. This transformation offers exciting new prospects for businesses and users alike.
Until recently, voice assistants were mainly utilitarian tools, executing simple commands and providing direct answers. But with advances in emotional artificial intelligence, these assistants go beyond simply understanding words: they perceive how we speak. By analysing tone, rhythm and other emotional cues, they can detect our emotional states. This opens the way to deeper human-machine interaction, where technology becomes a true mirror of our emotions.
1.1. The role of voice centres in improving the customer experience
Voice centres (voice-based assistance centres) have become a strategic lever for companies wishing to improve the customer experience. Traditionally, these centres were focused on resolving problems quickly. Today, thanks to the integration of voice-based emotional analysis, their mission is broader. By detecting emotions such as frustration or joy in a customer's voice, these centres can adjust their responses, modulate the tone of the conversation or transfer the customer to a human agent if necessary.

1.2. Emotional analysis of voice interactions
Semantic ia analysis of voice interactions is based on the detection of acoustic signals, such as the volume of the voice, the rhythm of speech, changes in tone, and even silences. Using emotional artificial intelligence technologies, these signals are interpreted to detect emotions such as sadness, joy, anger or confusion. This knowledge of emotions enables companies to adapt their interactions with their customers: they can adjust automated responses or modify the course of the conversation depending on the emotional state detected.
Voice assistants enhanced with this capability become not only more effective, but also more empathetic. For example, a voice assistant capable of detecting annoyance in a user's voice will be able to adjust its tone to become more soothing or offer a quicker solution. Emotional analysis in real time therefore offers greater personalisation of interaction, while increasing user engagement.
Integrating emotional recognition into voice assistants could profoundly transform the user experience. Imagine an assistant that detects your stress by hearing your tense voice, and automatically adapts its tone to be more comforting. Or an assistant that would suggest a relaxing playlist after sensing annoyance in your voice. The interaction would no longer be purely transactional, but would become empathetic, creating a genuine emotional connection between the user and the technology.
1.3. Limits and challenges of emotional speech analysis
Although emotional analysis of voice interactions has many advantages, it is not without its limitations. One of the main criticisms concerns the reliability of these systems. The emotions expressed by the voice can be influenced by various external factors, such as fatigue, stress or environmental noise, which can distort the interpretation of emotions.
Furthermore, the use of these technologies raises major ethical issues, particularly in terms of the protection of personal data. Voice emotion analysis represents a sensitive form of data, and companies need to ensure that this information is handled transparently and in compliance with current regulations, such as the RGPD in Europe. Otherwise, they risk losing the trust of consumers.
Finally, cultural and linguistic diversity poses an additional challenge, as the interpretation of emotions varies from one region to another, making it difficult to implement a universal emotional analysis.
2. Facial emotional analysis: an essential complement
Although voice analysis can detect certain emotions through the tone or rhythm of the voice, it has its limitations when it comes to capturing the entirety of a person's emotional state. Facial expression analysis is an essential complement to this understanding. Human faces convey an incredible wealth of emotion: a discreet smile, a frown or a simple glance can reveal feelings that words sometimes struggle to express. Thanks to recent advances in facial recognition, machines are now able to identify and analyse these micro-expressions, offering a more complete and nuanced view of emotion.
Integrating emotional facial recognition into interactions with automated systems, such as voice assistants or chatbots equipped with cameras, considerably improves the interpretation of users' emotions. Whether used to adjust the response of a virtual assistant in real time or to evaluate the effectiveness of a customer service interaction, facial analysis is a powerful tool for enriching theuser experience.
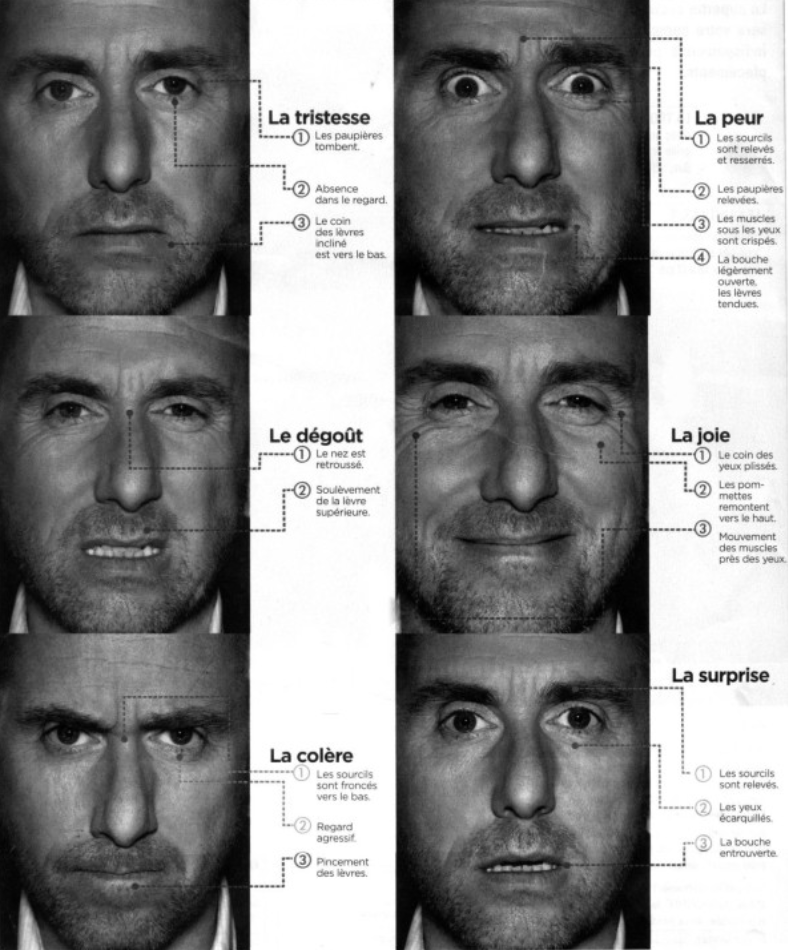
Primary emotions detected on facial muscles.
2.1. Facial expression recognition: technologies and applications
Facial recognition technologies are based on artificial intelligence algorithms that analyse and classify facial movements in real time. Usingmachine learning systems, the software learns to identify specific emotions based on databases ofuniversal human expressions. For example, muscles such as the zygomaticus major (associated with smiling) or the corrugator muscle (associated with frowning) are used to interpret emotions such as joy or anger. These analyses are particularly effective when integrated into customer interaction devices, such as chatbots or voice assistants equipped with cameras.
For businesses, facial expression recognition opens up new perspectives in customer relationship management. Systems equipped with cameras and facial analysis tools can pick up emotional signals that voice or text alone cannot. For example, a customer who appears satisfied through his or her words could actually be expressing frustration through a frown or a twitch of the jaw. By detecting these non-verbal signals, businesses are able to adjust their response in real time, offering a more empathetic and personalised interaction.
2.2. Integrating facial analysis into voice devices
When it comes to analysing emotions, it is essential to look beyond simple voice responses. Facial analysis, based on the identification of micro-expressions and subtle movements of facial muscles, is a valuable complement. These micro-expressions, often involuntary and of very short duration, reveal hidden or non-verbalized emotions such as anger, surprise or sadness. Thanks to sophisticated algorithms and machine learning, facial recognition technology can decode these signals in real time.
However, it is important to note that this approach is particularly useful in contexts where the voice alone is not enough to capture all of a user's emotions. For example, a customer whose vocal tone may appear calm could, in reality, be expressing irritation through tense facial muscles. Companies that integrate these tools into their interactions, such as chatbots with cameras or automated systems, benefit from a more complete emotional understanding. This capability not only makes it possible to adapt responses according to the user's mood, but also to improve the overall quality of interactions by making the experience more human and personalised.
2.3. Limitations and challenges of emotional facial recognition
However, integrating facial recognition to analyse emotions presents a number of challenges. The accuracy of this technology can vary depending on factors such as cultural differences, lighting conditions or camera resolution. In addition, there are ethical issues to be considered, notably the protection of privacy and the risks of non-consensual surveillance. It is therefore crucial for companies to adopt robust measures to guarantee the security and anonymity of the data collected, while complying with local regulations such as the RGPD in Europe. Despite these obstacles, facial expression recognition remains a promising technology for enriching emotional analysis and improving the customer experience.
3. Textual conversational data: understanding the emotions hidden in words
In digital interactions, textual exchanges account for a large proportion of conversational data. Whether through emails, online chats, comments on social networks or forums, analysing the emotions expressed through texts is becoming crucial for companies wishing to improve their understanding of customers. Unlike voice or facial interactions, text does not provide direct access to audio or visual clues to emotions, but it can contain a multitude of subtle elements that allow us to detect the emotional state of users. This section explores the importance of contextualisation, concrete applications in customer service, and Q°emotion's response to these needs.
3.1. Detecting emotional changes in conversations
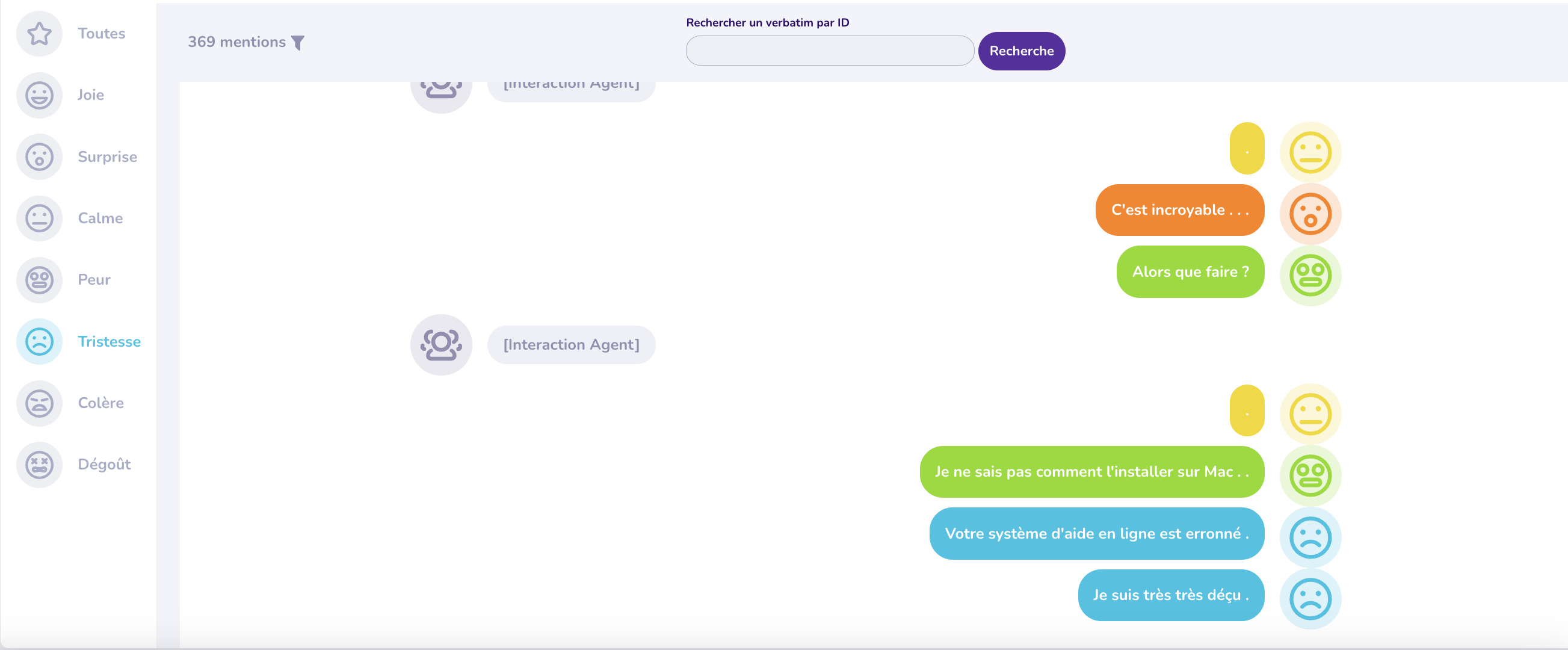
Speech to text conversation between customer (right) and agent: Q°emotion 2023 After Sales Demo Project
Detecting emotional changes during a conversation is essential for understanding changes in a user's mood and adapting responses accordingly. For example, a customer who begins by expressing frustration may, if their problem is resolved satisfactorily, show signs of relief or satisfaction as the conversation progresses. The ability to track these emotional variations in real time enables companies to adjust their response in a more tailored and personalised way, making the customer experience much smoother and more positive.
Emotional analysis technologies, such as those offered by Q°emotion, are capable of capturing these changes in mood using natural language processing (NLP) algorithms. These tools analyse not only the words used, but also sentence structure and tone to detect subtle clues to emotional transition. For example, short, dry sentences may indicate rising frustration, while a more developed, calm response may reflect emotional improvement.
3.2. Practical applications of emotional analysis in customer services
In customer services, emotional analysis of text conversations is a cornerstone of customer satisfaction. Companies receive thousands of messages via email, online chat or social platforms. The challenge is to be able to process this information efficiently while identifying the emotions behind the words. This ability to understand the emotional state of customers in real time makes it possible to personalise interactions and prevent crises.
For example, an e-commerce company may receive an e-mail from a dissatisfied customer about an order. Emotional text analysis can detect signals of anger or frustration, even if the customer does not directly use explicit terms. By reacting proactively, such as offering a quick solution or compensation, the company can turn a negative experience into an opportunity to build customer loyalty. What's more, in online chats, where responses need to be quick, emotional analysis can immediately detect potentially frustrated customers and guide the conversation to defuse the conflict. (cxinsights.io reporting module).
Using tools like Q°emotion in customer services can significantly improve the customer experience, speed up problem resolution and strengthen the relationship with users. By detecting the emotions underlying text messages, companies can adjust their responses and show greater empathy, which is crucial in online interactions.
3.3 How Q°emotion meets these needs
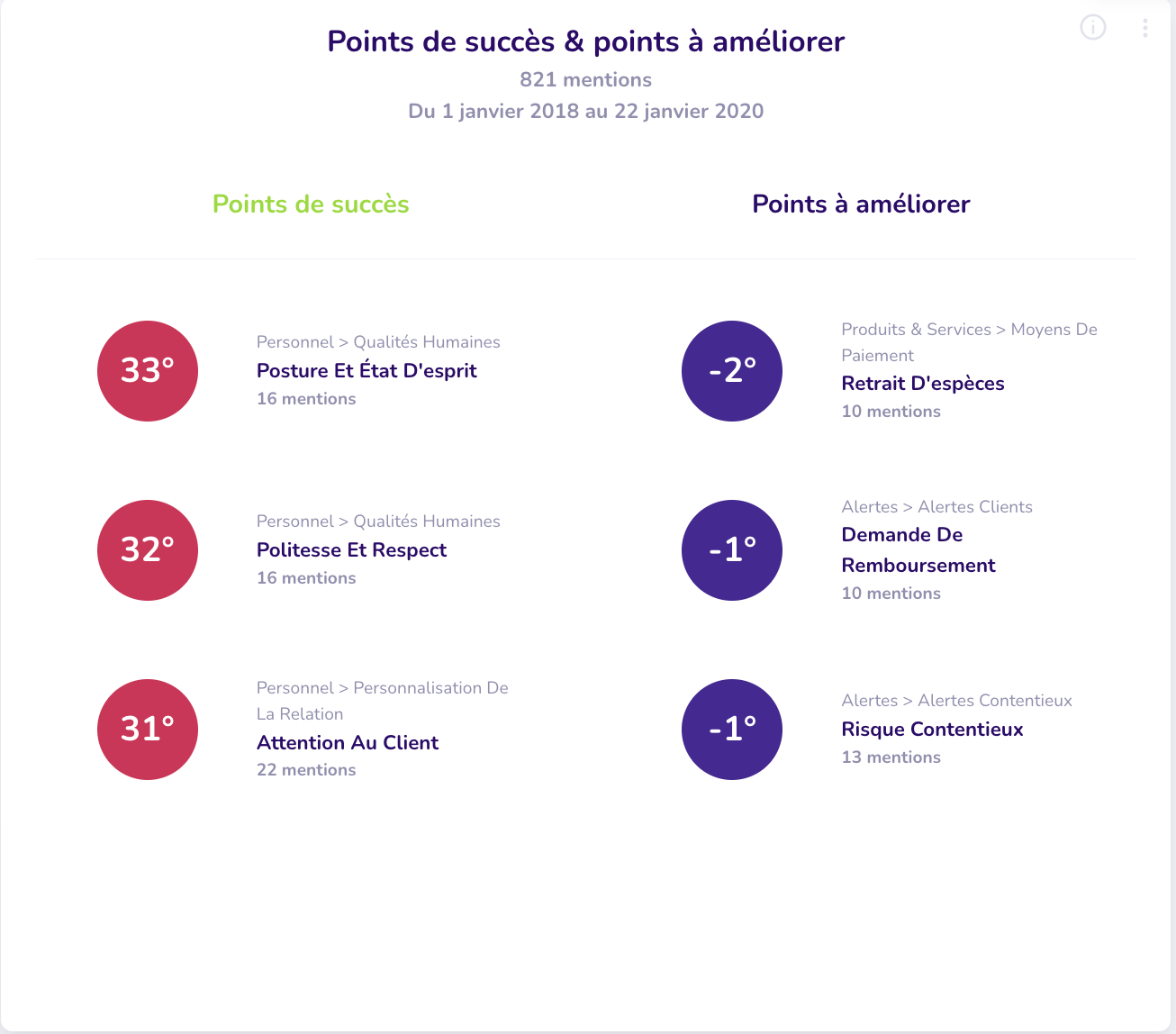
Q°emotion 2022 Demo Bank Project
Q°emotion stands out for its ability to analyse emotions from textual data by combining cutting-edge technologies in semantic artificial intelligence and natural language processing. Its platform makes it possible to analyse emotions expressed in texts in real time, whether via emails, online chats or comments on social networks, and to extract emotional information that is relevant to businesses.
Thanks to its advanced algorithms, Q°emotion identifies the main emotions, such as joy, sadness or anger, but also more subtle emotional themes. This enables companies to better understand their customers' emotional expectations and adapt their responses to offer more personalised and relevant interactions.
What's more, Q°emotion's platform integrates easily with customer relationship management (CRM) systems and customer support tools, offering businesses a complete solution for capturing their customers' emotions across a range of text-based channels. By providing emotional insights in real time, Q°emotion helps businesses make quick and informed decisions, improving customer satisfaction and long-term loyalty.
Conclusion: When AI understands emotions.
Voice assistants and facial analysis tools are rapidly evolving towards a more emotional and personalised interaction model. This evolution doesn't just make the technology more efficient; it makes it more human. By working with emotional analysis experts like Q°emotion, companies can not only anticipate their customers' needs, but also create more emotionally engaging experiences. This could well be the next big shift in the way we interact with technology - one where machines don't just respond, but actually listen and understand.
If you'd like to find out more about our emotional analysis tools and how you can turn your customer feedback into valuable information, visit our blog or contact us!
Similar posts
Customer Experience vs. Customer Success: Understanding the differences and maximising customer loyalty through emotional analysis
Published on October 29, 2024 - Updated on November 04, 2024
In an increasingly competitive business environment, companies must now redouble their efforts to capture and retain customers. According to a recent study by Forrester , 73% of companies now...
Reduce holiday stress with Q°emotion: How brands can manage customer emotions over Christmas
Published on October 29, 2024 - Updated on February 14, 2025
Reduce holiday stress with Q°emotion: How brands can manage customer emotions over Christmas Introduction: The Christmas paradox Although Christmas is traditionally a time of joy, sharing and celeb...